Kalle - Blog
Leveraging AI for Business: The Importance of Human Contribution in Copyright Protection

As businesses increasingly explore the use of AI-generated designs and art, it's crucial to understand the nuances of copyright protection in this evolving field. While AI can produce bulk images efficiently, the legal framework around intellectual property rights (IPR) remains clear: significant human involvement is key to securing copyright protection. This is particularly important for businesses looking to protect their brand identity and creative assets.
The Role of Human Contribution in Copyright Protection
In Europe, copyright laws are rooted in the principle that only works with a meaningful human contribution can be protected. This means that while AI can generate impressive visuals, these creations often cannot be copyrighted unless a human author is substantially involved. The European Union's legal framework, including guidance from the European Parliament, emphasizes the necessity of human creativity in the creation process.
For businesses, this distinction is crucial. Using AI to generate a large volume of generic images may save time and resources, but these images might not qualify for copyright protection. This could leave businesses vulnerable to imitation and misuse. To safeguard valuable designs, it is advisable to involve a professional artist or designer who can infuse the work with a unique human touch. This not only enhances the originality and quality of the content but also strengthens the case for copyright protection.
Strategic Use of AI and Human Talent
For high-stakes projects, such as branding or product design, combining AI's efficiency with human expertise offers the best of both worlds. An artist or designer can guide the creative process, ensuring that the final output reflects the business's vision and adheres to legal standards for copyright eligibility. This hybrid approach allows businesses to leverage AI's capabilities while still benefiting from the nuanced artistry and judgment that only humans can provide.
Moreover, businesses should consider the broader implications of using AI-generated content. Engaging with skilled professionals ensures that the creative output aligns with the brand's identity and values, offering a consistent and authentic customer experience. This strategic collaboration can also foster innovation, as human creativity often leads to unexpected and original solutions that AI alone may not produce.
Conclusion
In the context of intellectual property rights, businesses must carefully navigate the use of AI-generated art and design. While bulk images generated by AI can serve functional purposes, important projects demand the touch of a skilled artist or designer to secure copyright protection and maintain brand integrity. By understanding the legal landscape and strategically combining AI with human talent, businesses can create unique and protected visual assets that stand out in the market.
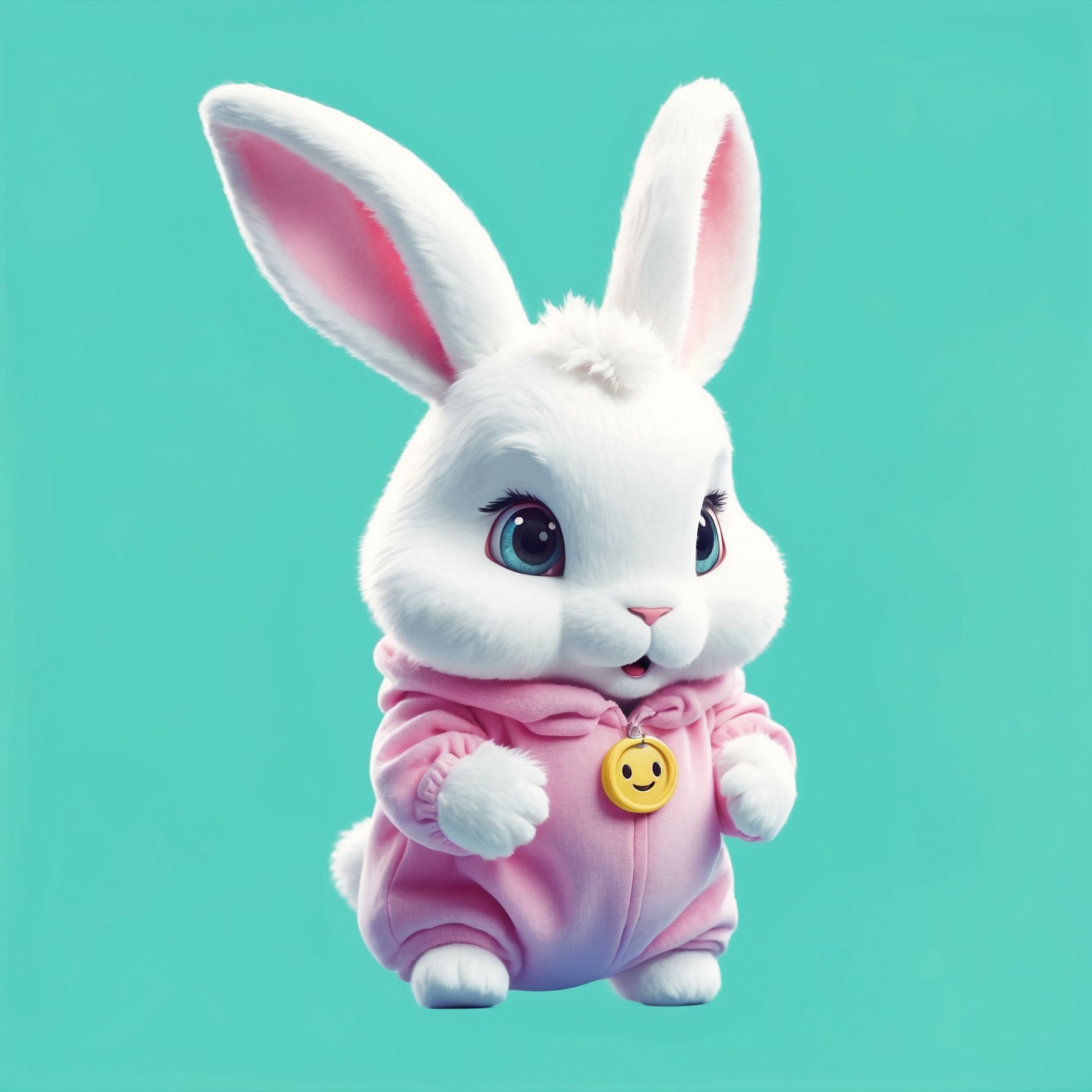
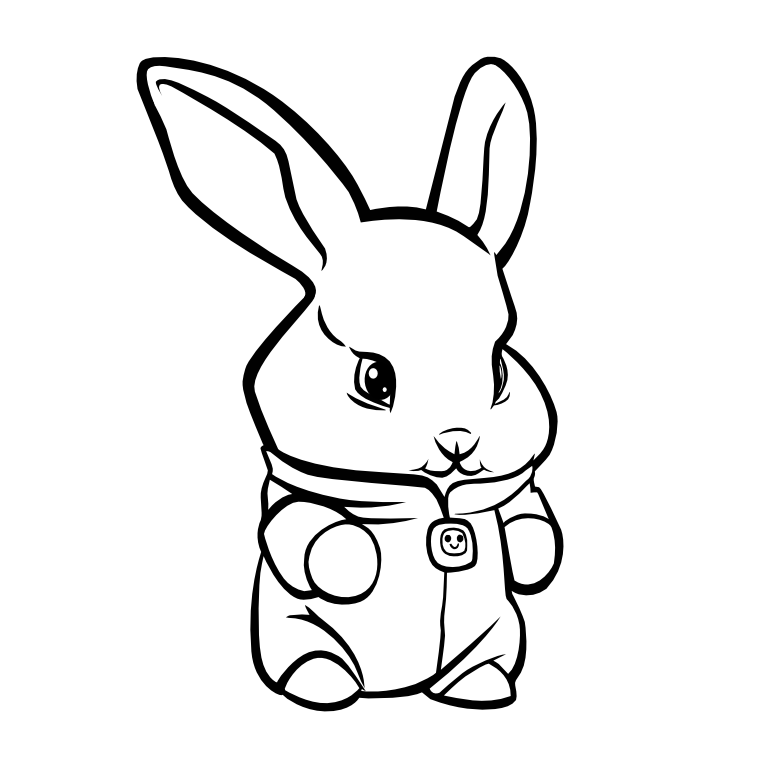
An example of how to protect intellectual property rights (IPR) could involve the following scenario: The first image is a black-and-white handmade drawing of a bunny. The second image is an AI-generated version based on the original drawing.
In this case, the original drawing is protected by copyright due to its human authorship. The AI-generated image, if it significantly involves substantial human input in the creation process, it also qualify for copyright protection. This dual-layer approach ensures that both the initial concept and the subsequent AI-enhanced version are protected, safeguarding the creative assets and intellectual property of the creator or business.
All Rights Reserved | Kalle Erkkilä
Site published 24th of November 2018. v2.0